Spring Boot Metrics
In this post I’ll discuss how to monitor spring boot application metrics using Prometheus and Grafana.
Prometheus
Prometheus is a monitoring system which collects metrics from configured targets at given intervals.
Grafana
Grafana is an open source metric analytics & visualization tool.
Micrometer
Micrometer is a metrics instrumentation library for JVM-based applications.
Spring Boot Actuator
Spring Boot Actuator helps you monitor and manage your application when it’s pushed to production. You can choose to manage and monitor your application using HTTP or JMX endpoints.
Setup
Enable prometheus metrics by adding dependencies in pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId>
<version>1.0.6</version>
</dependency>
By default prometheus endpoint is not available and must be enabled in application.properties. More configurations can be found at spring-boot docs
#Metrics related configurations
management.endpoint.metrics.enabled=true
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.prometheus.enabled=true
management.metrics.export.prometheus.enabled=true
management.metrics.distribution.percentiles-histogram.http.server.requests=true
management.metrics.distribution.sla.http.server.requests=1ms,5ms
management.metrics.distribution.percentiles.http.server.requests=0.5,0.9,0.95,0.99,0.999
Optionally register any number of MeterRegistryCustomizer to further configure the registry (such as applying common tags) before any meters are registered with the registry.
@Bean
MeterRegistryCustomizer<MeterRegistry> metricsCommonTags() {
return registry -> registry.config().commonTags("application", "sample-app");
}
Create a new project; deploy the application and prometheus in OpenShift.
$ oc project myproject
$ oc new-app redhat-openjdk18-OpenShift~<git_repo_URL> -n sample-app
oc new-app prom/prometheus -n prometheus
In order to keep the prometheus image and configuration decoupled, use the ConfigMap object to inject our the Prometheus deployment with the appropriate configuration data
cat <<'EOF' > prometheus.yml
global:
scrape_interval: 5s
evaluation_interval: 5s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'sample-app'
metrics_path: '/actuator/prometheus'
static_configs:
- targets: ['sample-app:8080']
EOF
oc create configmap prom-config-example --from-file=prometheus.yml
Next, edit the deployment configuration for Prometheus to include this ConfigMap.
oc edit dc/prometheus
Add new volume and volume mount
- name: prom-config-example-volume
configMap:
name: prom-config-example
defaultMode: 420
- name: prom-config-example-volume
mountPath: /etc/prometheus/
Use an OpenShift Template to run Grafana with persistent storage.
$ oc process -f https://gist.githubusercontent.com/Vikaspogu/4a67495acf8dba5dc94837e031129fde/raw/e88f42515c6ed101c9554c7c2425794e80e10a64/OpenShift-grafana.yaml | oc apply -f-
Once deployed, log-in to Grafana using the Route provided in the Template and using default account admin with password admin (it maybe a good idea to change the password after this).
Grafana Data Source
-
The Grafana template automatically provisions a Prometheus data source
App-Prometheuswhich connects tohttp://prometheus:9090via proxy connection. -
This works only if there is a Prometheus service (called prometheus) in the same project as Grafana. If this is not the case, it is necessary to edit the datasource to point to another location.
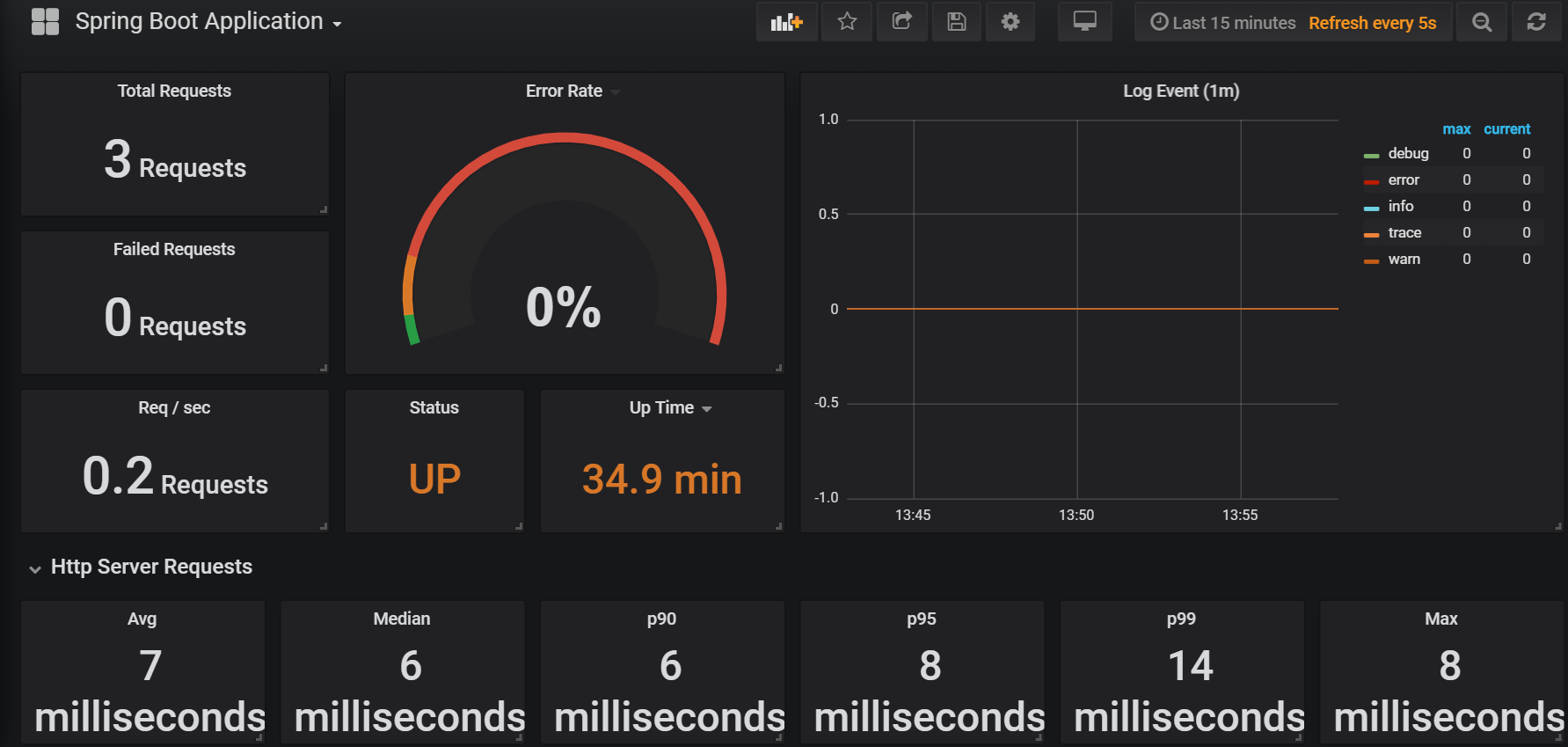
Grafana Dashboard
- The Grafana template automatically provisions sample dashboards. These dashboards are by no means comprehensive but could be used as a starting point for further customization.
You can find more official & community built grafana dashboards here