Recently I was working on a React project with Go backend using Gin web framework. Keycloak was the authentication mechanism for the frontend; I also wanted to secure the backend using JSON Web Tokens which was provided by Keycloak on every login. Setup for jwt verification in Go was easy.
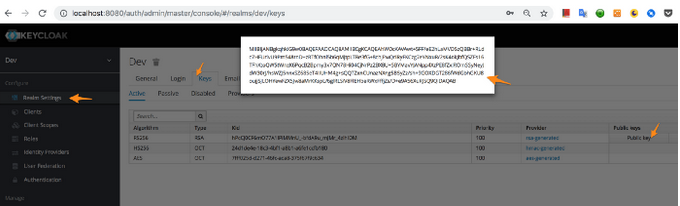
First, copy RS256 algorithm public key value from Keycloak
Send the token as Authorization header
axios
.get(BACKEND_URL.concat("sampleendpoint"), {
headers: {
Authorization: this.state.token
}
})
.then(res => {});
Now Go-backend setup; let’s install the jwt-go, gin-cors libraries:
go get -u github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go
$ go get -u github.com/gin-contrib/cors
Add cors config to the router to allow authorization header
router.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{
AllowOrigins: []string{"*"},
AllowMethods: []string{"GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "OPTIONS", "HEAD"},
AllowHeaders: []string{"Origin", "content-type", "accept", "authorization"},
ExposeHeaders: []string{"Content-Length"},
AllowCredentials: true,
MaxAge: 12 * time.Hour,
}))
Let’s create a custom handler; add the public key from Keycloak and pass it to ParseRSAPublicKeyFromPEM which will return a key. The key and token are then validated
func VerifyToken(c *gin.Context) {
SecretKey := "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n"+
"MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEApn
......
+wnyuCHaCHp8P1yCnwIDAQAB" + "\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----"
reqToken := c.GetHeader("Authorization")
key, er := jwt.ParseRSAPublicKeyFromPEM([]byte(SecretKey))
if er != nil {
fmt.Println(er)
c.Abort()
c.Writer.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
c.Writer.Write([]byte("Unauthorized"))
return
}
token, err := jwt.Parse(reqToken, func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) {
// Don't forget to validate the alg is what you expect:
if _, ok := token.Method.(*jwt.SigningMethodRSA); !ok {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Unexpected signing method: %v", token.Header["alg"])
}
return key, nil
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
c.Abort()
c.Writer.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
c.Writer.Write([]byte("Unauthorized"))
return
}
if _, ok := token.Claims.(jwt.MapClaims); ok && token.Valid {
fmt.Println("token is valid")
}
}
Add the handler to the route
router.GET("/sample", VerifyToken(), handlers.SampleEndpoint)
That’s, it done, If the token is valid, you will get the data from backend or else you’ll see 401 Unauthorized